Modern Art: Late 19th century to mid-20th century | Artists experimented with new techniques, moving away from traditional Indian art forms. They combined Indian cultural identity with Western styles like impressionism and cubism. The themes often focused on nationalism and the struggle for independence.
Contemporary Art: Time Period: Mid-20th century to the present | Contemporary Indian artists use a variety of mediums, including digital and installation art. Their work is more experimental, often addressing global issues like urbanization, identity, and technology.
Understanding the Difference Between Modern Art and Contemporary Art: An Indian Perspective
The terms modern art and contemporary art are often used interchangeably, but they represent distinct periods, philosophies, and practices in the world of art. Both movements hold unique significance in shaping the country’s art landscape. With India’s rich cultural heritage and evolving art scene, this distinction becomes even more meaningful in appreciating the depth & diversity of Indian artistic expression.
What is Modern Art?
Modern art generally refers to artistic works produced between the late 19th century and the mid-20th century. It marked a radical departure from the traditions and techniques of classical and academic art, focusing on innovation and experimentation. Artists during this period challenged conventions, and their work often reflected the social, political, and technological changes of the time.
In the Indian context, modern art emerged during the late colonial period, around the early 20th century. Pioneers like Rabindranath Tagore, Amrita Sher-Gil, and the Progressive Artists’ Group, which included figures like M.F. Husain, F.N. Souza, and S.H. Raza, played a significant role in this movement. They sought to break away from the colonial and academic art styles imposed by the British and embraced both indigenous traditions & international influences to express new ideas about Indian identity, culture, and modernity.
Modern Indian art often revolved around themes of nationalism, cultural identity, independence, and the struggle for freedom. It was a period of artistic innovation where Indian artists explored traditional techniques while simultaneously incorporating Western styles like impressionism, surrealism, and expressionism. This blend of influences gave rise to a distinctive voice in Indian art.
What is Contemporary Art?
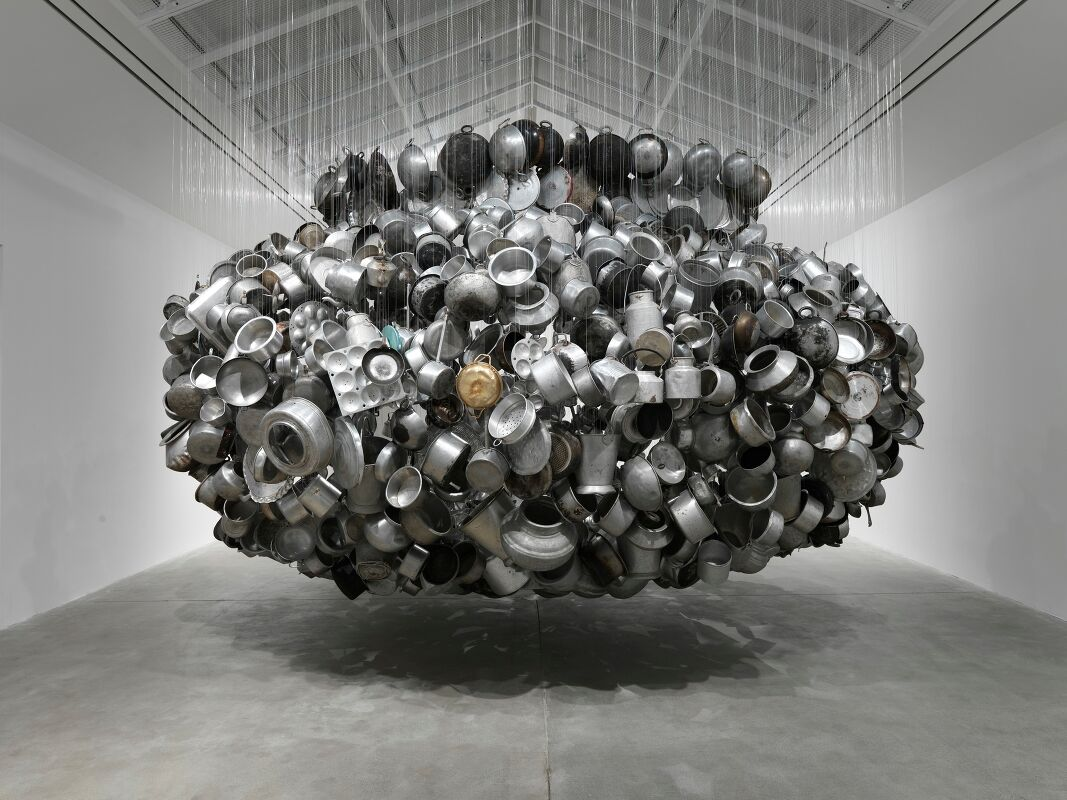
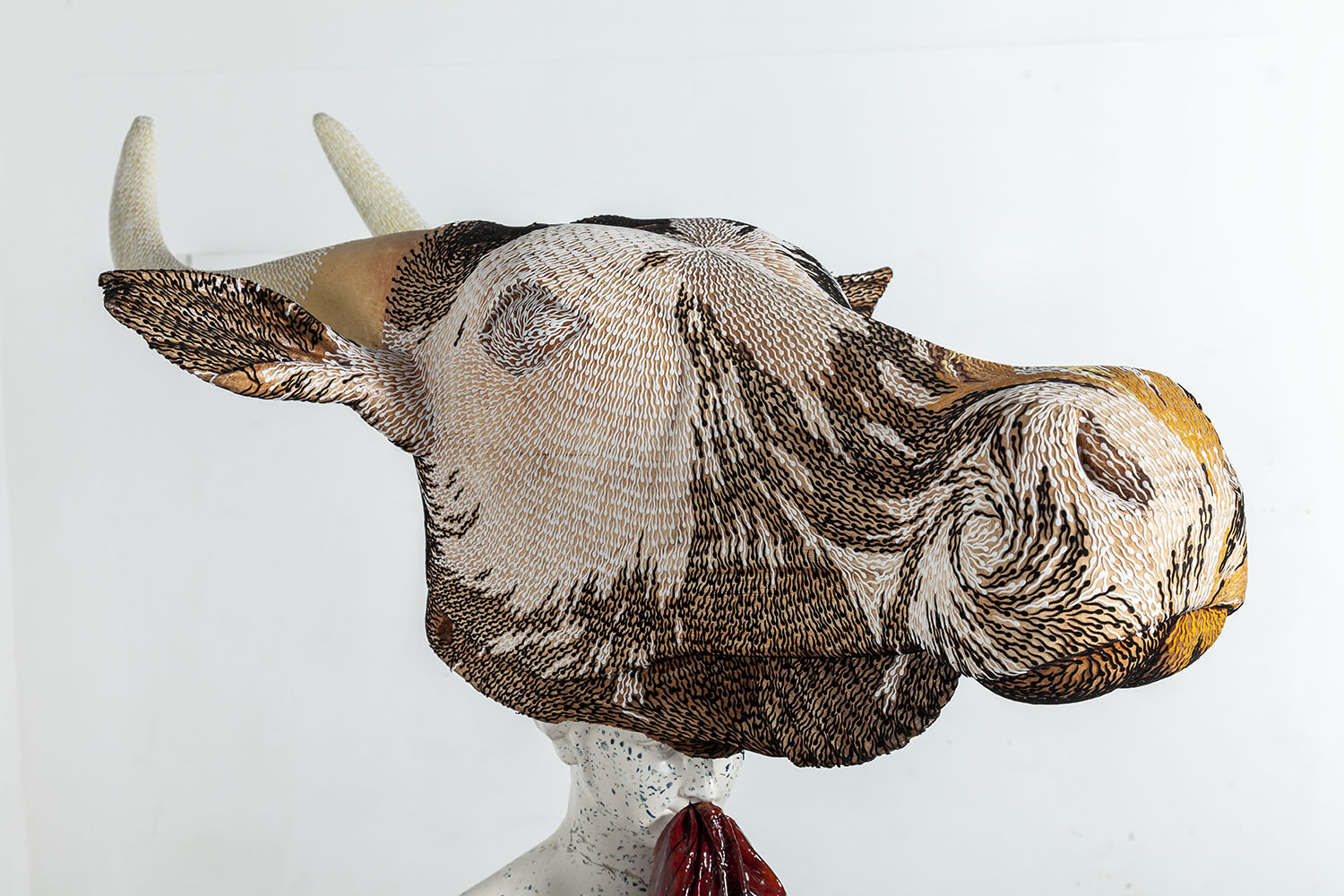
Contemporary art, on the other hand, refers to art produced in the present day—from the mid-20th century to today. Contemporary artists focus on reflecting the complexities of modern life, often pushing the boundaries of what is considered art by exploring new media, techniques, and ideas. It is a more fluid and diverse movement that incorporates everything from painting and sculpture to digital art, installation, and performance.
In India, contemporary art mirrors the country’s rapid socio-economic and cultural changes. Artists like Subodh Gupta, Bharti Kher, and Jitish Kallat are globally recognized for their innovative works that address topics like globalization, identity, gender, and technology. Contemporary Indian art is characterized by a mix of traditional motifs with global narratives, often challenging viewers to reconsider what art can be and how it interacts with society.
One defining feature of contemporary Indian art is its engagement with both local and global issues. While Indian culture, mythology, and spirituality remain central to many artists’ works, there is also a focus on broader issues like environmental change, urbanization, migration, and the politics of identity. Unlike modern art, which had a distinct timeline and ideological framework, contemporary art is constantly evolving, reflecting the world’s ever-changing landscape.
Key Differences
- Timeline:
- Modern Art: Roughly from the late 19th century to the mid-20th century.
- Contemporary Art: From the 1960s/1970s to the present day.
- Themes:
- Modern Art: Explored nationalism, independence, cultural identity, and modernization.
- Contemporary Art: Engages with a wider range of subjects, including identity, globalization, environment, technology, gender politics, and social change.
- Art Forms / Media:
- Modern Art: Primarily paintings, sculptures, and drawings using traditional media but with new forms and styles like abstraction, surrealism, and cubism.
- Contemporary Art: Incorporates installation, performance art, digital media, video art, and interactive works. It is more experimental and open to unconventional forms of expression.
- Philosophy:
- Modern Art: Focused on breaking away from classical and academic traditions. Emphasis on innovation and personal expression, with a clear historical narrative often tied to nationalism and identity in the Indian context.
- Contemporary Art: Diverse and dynamic, with no single defining philosophy. It reflects current global and local issues, using various forms of media and techniques, including digital and conceptual art.
Why should this matter for Art Students, Art collectors or Art connoisseurs?
India’s art scene has undergone a fascinating evolution, from the historical temples and miniature paintings to the bold, experimental works of today’s artists. Understanding the difference between modern and contemporary art allows viewers to appreciate the historical context of each work and its relevance to current social and political issues.
In today’s globalized world, contemporary Indian artists are not confined to their national context. Their work engages in international dialogues, addressing issues like migration, diaspora, and the blending of cultures. This transition from modern to contemporary art reflects India’s journey through colonization, independence, globalization, and rapid modernization. While modern art was about forging a new identity and breaking free from colonial influence, contemporary art explores the complexities of modern life in a rapidly changing world. Recognizing this trajectory helps Indian art enthusiasts and collectors understand shifts in artistic practices and the importance of innovation, enriching their appreciation of the evolving artistic landscape.






Leave a Reply